 Since heart disease, stroke and peripheral vascular disease are such prominent causes of chronic ill health and death in our society, prevention is the key.
Since heart disease, stroke and peripheral vascular disease are such prominent causes of chronic ill health and death in our society, prevention is the key.
The keys to prevention are calorie restriction (don’t overeat) and regular physical exercise involving a combination of aerobic conditioning, muscle building and stretching. Also important, are the regular consumption of a good multivitamin and mineral supplement, and the intake of additional calcium and magnesium.
The diet should be rich in green and other colourful vegetables, which are high in fibre. Also, include the regular intake of high-quality proteins from lean meats with restricted intake of saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and processed foods. The daily intake of a small amount of alcohol also reduces risk, e.g. a glass of wine at dinner.
As well, annual physicals with the family doctor to have blood pressure monitored and blood tests done to check cholesterol profile and blood glucose are very important. Early management for high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels and diabetes are vital in the prevention of cardiovascular disease in the future.
With established disease, nutritional intervention and a proper exercise program are still very important. Presently, the use of modern pharmaceutical drugs such as statins (to reduce cholesterol) and ACE inhibitors (to help improve heart contraction and produce vascular remodelling) have reduced mortality in patients with established cardiovascular problems.
However, the use of these drugs may prolong life but not improve the quality of life and do have side effects. Therefore, the appropriate intake of nutritional supplements can really help improve one’s energy and well-being. For instance, the regular use of Coenzyme Q 10 improves energy production in cells and cardiac function. It reduces the side effects of statins, which lower Coenzyme Q 10 levels in the blood. The intake of antioxidants such as vitamins E and C and selenium protects the vascular wall lining. The use of chromium improves the regulation of blood sugar, and an adequate intake of magnesium regulates blood pressure and reduces spasm of the arteries.
A high intake of vitamin B12, folic acid and vitamin B6 lowers the level of homocysteine in the blood. Hemocysteine is a substance, which damages the vascular wall over time. Therefore, the use of these vitamins in a multivitamin and mineral supplement, as a preventive measure, is important.
Besides the use of low dose aspirin to reduce the aggregability of the blood, the intake of bromelain and turmeric (found in curry and as supplements) is helpful. Ginger is another spice useful for reducing platelet aggregation.
The employment of a treatment called EDTA chelation therapy is very beneficial in improving perfusion of the heart with oxygen, reducing calcium build up in the vascular wall and reducing free radical stress. Its use in the cardiovascular patient is a powerful adjunct to the information above.
Smoking cigarettes is one lifestyle factor that must be addressed. Cigarettes are a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and its cessation is vital in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular problems.
Chelation Therapy: A Treatment For Heart Disease
 What is Chelation?
What is Chelation?
Chelation comes from the Greek word “chele” meaning claw. A chelating compound binds and removes heavy and other toxic metals from the body. There are many chelating agents used in medicine. EDTA Chelation therapy is the intravenous administration of a man-made chelating agent called Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic-Acid. This substance binds to heavy metals in the body and allows them to be safely excreted by the kidneys.
What are the benefits of Chelation therapy?
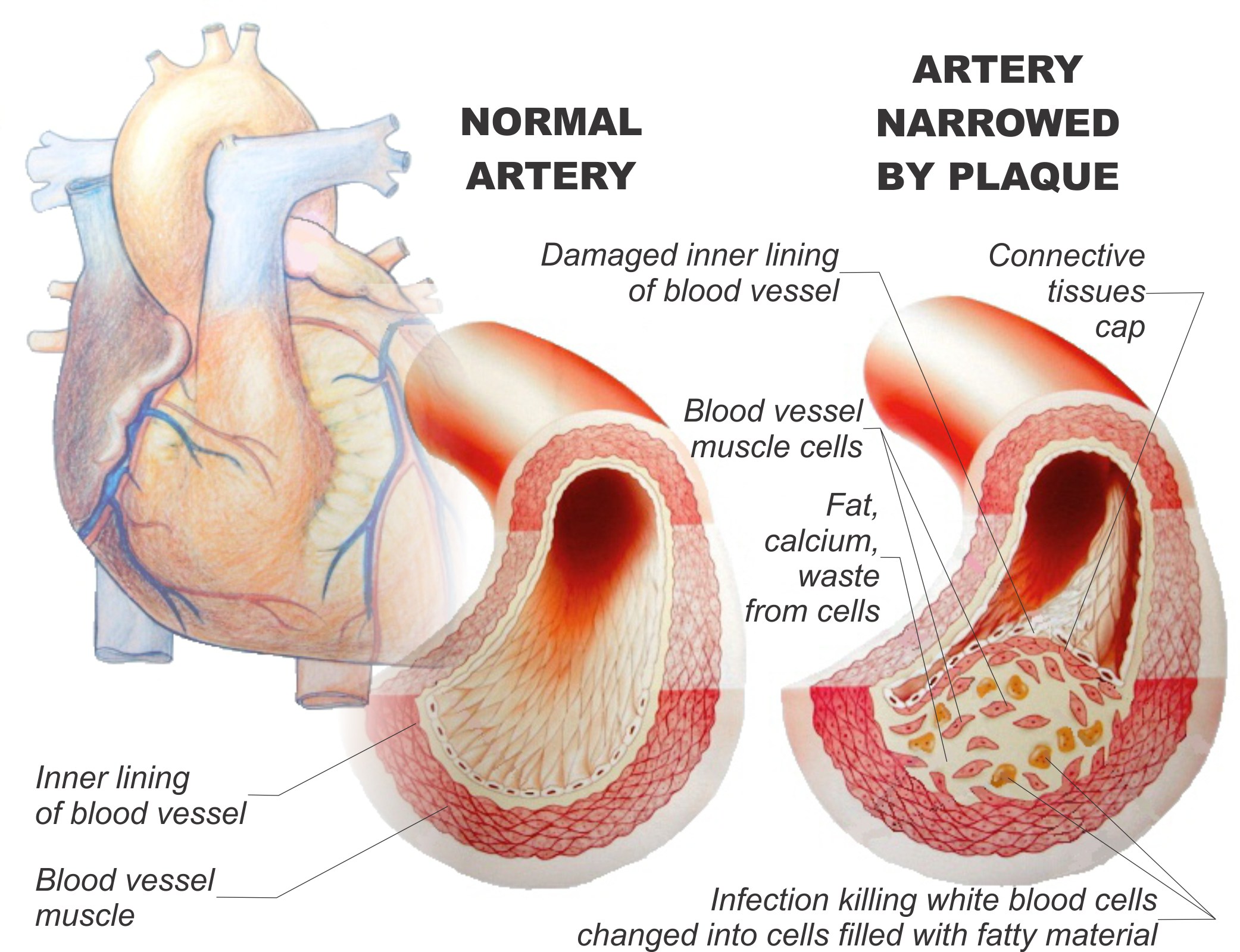
EDTA removes harmful metals that are implicated in cardiovascular disease. When given as magnesium EDTA, the substance gradually breaks down calcium deposits that form on the artery walls. It also lowers calcium levels. Calcium is involved in the formation of blood clots. The mechanism of the two actions results in the greater flexibly of blood vessels. The removal of harmful metals decreases the damage caused by free radicals on the artery walls. EDTA Chelation therapy can also be used in the treatment of degenerative conditions, which are conditions that are characterized by a progressive decline in health. These include scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
How is Chelation therapy administered?
Treatment is administered intravenously. A small needle is inserted into the vein – often on the back of the hand. The treatment lasts three hours while the patient is comfortably seated. Chelation therapy works best when integrated with a good diet, nutrients and lifestyle changes. A thorough evaluation of each patient by the medical doctor is performed and an individualized nutritional program is prescribed.
How often are the treatments needed and for how long?
Because Chelation works over time, a number of treatments have to be administered. The course of the treatments are once to twice weekly for 30 treatments, then once a month for 12 months followed by every three months as part of a maintenance programme.
Are there any side effects of Chelation therapy?
Chelation therapy is very safe when given by the correct protocol. It has been used many hundreds of thousands of times over the last half-century. Few side effects have been reported; however, as with any medical treatment, reactions can occur. It is for this reason that patients are closely monitored. Upon beginning a chelation programme, the patient’s own cardiologist/family doctor should be informed. Medical therapy, as prescribed by the patient’s personal physician, is continued. Often, over time, some medical therapy can be reduced and even stopped. The discontinuation of prescribed medical therapy is assessed by close medical monitoring.
History of Chelation
Chelation therapy goes back 50 years when it was noted that patients being treated for lead poisoning using EDTA showed unexpected dramatic improvements in their atherosclerotic circulatory disorders. An international study on the safety and effectiveness of Chelation therapy was launched in 2003. This study has been sponsored by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) in the United States. Hundreds of medical institutions across North America are taking part in it. Prior research to this study showed an improvement in over 80% of the patients. (Ref. Journal of Advancement in Medicine, vol 7, number 3, Fall 1994, page 131).
Related articles
Cardiovascular Chelation
Chelation Therapy: A Treatment for Blocked Arteries
Heavy Metal Detoxification